Use the <R> option to remove all bolding on the line. See also
SELECT BOLD/UNDERLINE.
|
|
| Purpose: |
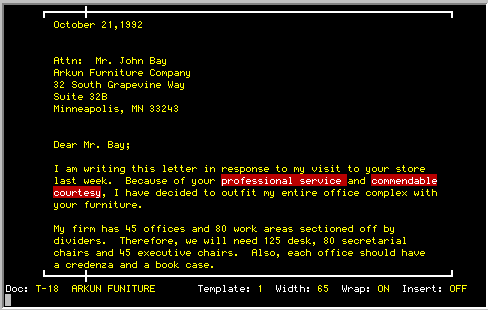
Repositions text on current line in the center
with equal space to the left and right.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FORMAT LINE function key,
<C> to select CENTER
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor on the line that is
to be
centered and press the <FORMAT LINE> key. Now press <C> to
select the
CENTER command. The line will be centered on the screen and the cursor
will drop down one line. Pressing the letter <C> again will center
the
next line, and so on. To return to Edit Mode, press <RETURN>.
Centered text can be brought back to the left margin using the
LEFT-JUSTIFY
command.
Centered text on the CRT screen will not always be centered on the paper
when using proportionally spaced fonts. In many cases, this can be
remedied by including a ~ CT somewhere in the line that is to be
centered.
When using the ~ CT function, the text does not need to be centered on
the screen to have the text centered on the printer.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
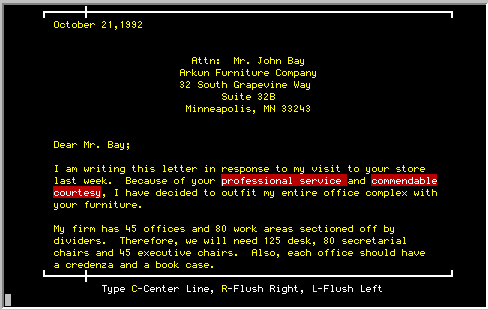
Enables one or more occurrences of
a word or
phrase within a document to be changed without finding each one and
retyping it.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
OTHER OPTIONS function key, select
CHANGE EVERY
from Other Options menu, press <RETURN>
|
| How Is It Used: |
Once the CHANGE EVERY command has
been selected,
enter the word or phrase to be replaced and press <RETURN>.
Then enter the word or phrase to replace with and press <RETURN>.
If the cursor is not at the beginning of the document, you will be asked
whether the search and replace operation is to start at the current cursor
position or at the beginning of the document. Enter <H> for HERE or
<B> for BEGINNING.
To halt the CHANGE EVERY operation press any alphanumeric key.
NOTE: Only whole words may be changed with this
command. Parts of words or hyphenated words will not be included. Use
WORD SEARCH and the editor for these type of changes.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Removes a single character at the cursor position.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
CHARACTER DELETE key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Pressing the <CHARACTER DELETE> key will cause the
character at the current cursor position to be deleted and replaced by the
character immediately to its right. All other characters on the right
will move one space to the left.
If the cursor is beyond the end of the line, pressing the <CHARACTER
DELETE> key will cause the next line down to be joined to the current
line
at the cursor position or one space from the last word, whichever is
furthermost to the right.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Inserts a space in the text at the current cursor position.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
INSERT CHARACTER key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Pressing the <INSERT CHARACTER> key causes a
single space to be inserted at the cursor position and any characters to
the right to be moved one space to the right.
If the last character on the line is pushed off of the end of the line
because of a CHARACTER INSERT operation, the entire last word will be
removed and inserted on the next line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows multi-national characters to be typed from any keyboard..
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
Control B, W, or Z (depending upon operating environment)
|
| How Is It Used: |
There are two methods of using the Compose key:
1. With new text - In typing new text and you reach a spot
where you need
to type a multi-national character, press the Compose Key followed by a
two
letter sequence indicating somewhat symbolically the desired
multi-national
symbol. The following are valid examples:
|
| | First letter |
Second letter
| A | `'"~ ^eo
| C | ,
| E | `'"^
| I | `'^"
| N |
| | O | `'^~ "E/
| U | `'^"
| Y | "
| a | `'^~ "oe
| c | ,
| e | `'^"
| i | `'^"
| n |
| | o | `'^~ "e/
| s | s
| u | `'"^
| y | "
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Note that some terminals already have a compose key built into the
terminal
firmware. It is certainly permissible for you to use this feature also if
it is available to you. Terminals that do not support multi-national
character sets cannot be used with the Compose Key feature.
2. With old text - Pressing the Compose Key while the cursor is
already
sitting on one of the letters illustrated in the first column will cycle
through each of the various multi-national (diacritical and diagraphical)
forms.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Enables one or more lines of text to be
copied to
another position in the same document or any other document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
COPY/MOVE/INSERT function key,
<C> to COPY
|
| How Is It Used: |
Begin the operation with the cursor on
the first
character of the text to be copied. Press the <COPY/MOVE/INSERT>
function key and select COPY by pressing <C>.
The current screen will be redisplayed in low intensity. Highlight the
text to be copied using the cursor keys which work as follows:
|
| | Left |
Removes one word from the text to be copied, and changes it back to
low intensity.
| | Right |
Adds one word to the text to be copied and highlights it.
| | Up |
Removes a whole line from the text to be copied and changes it
back to low intensity.
| | Down |
Adds one line to the text to be copied and highlights it.
|
Notice that the <LEFT> and <RIGHT> cursor keys provide
word control, while the <UP> and <DOWN> cursor keys
provide line control. With a little
practice, you will be able to quickly highlight a region of text using the
appropriate cursor keys.
Press <RETURN> when the text to be copied has been highlighted.
At TK-WRITER's request, assign a name to the highlighted text. Use a name
that will be easily remembered if you are likely to use this copied text
over and over again. You may use the 26 letters of the alphabet and the
10 numbers. Press <RETURN> when the name is entered.
The following display provides an example of a name being assigned
to a section of highlighted text:
You will then be reminded that this copied text can be inserted with the
INSERT TEXT command of the same <COPY/MOVE/INSERT> function key.
Press "RETURN" to return to the edit mode. See INSERT TEXT for information
concerning inserting the text in the current document or in another
document.
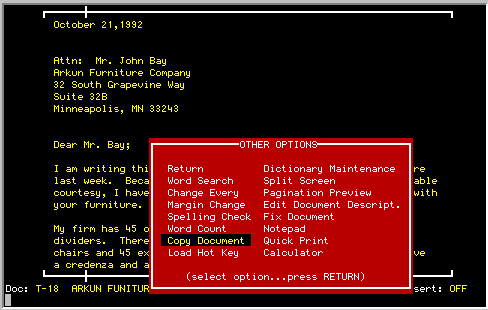
Entire documents can be copied with the Copy Document option from the
Special Options menu as illustrated below:
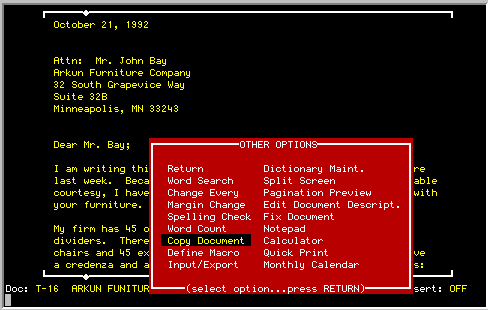
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Permits fine movement within the document either
left or right or up or down.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
UP, DOWN, LEFT, or RIGHT cursor keys
|
| How Is It Used: |
The cursor keys permit movement of one space forward or backward,
or one line up or down.
The action taken by the cursor changes when the margins of the screen are
reached. Up and down movements at the top or bottom margins will cause a
single line scroll operation to take place. Left and right movements at
the left or right margins will cause the cursor to wrap around to the
opposite margin on either the next or preceding line.
The cursor keys take on a different meaning while in the COPY/MOVE TEXT
commands. They are used to select or deselect text.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows the user to break a line of text for the purpose of adding
more text or changing the format.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
CUT LINE function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor at the beginning of the text to be cut from the
current line and press the <CUT LINE> key. The character under the
cursor and the remainder of the line to the right of the cursor will be
moved to the next line.
Note that the CUT LINE function also provides a quick way of opening up a
few lines directly below the typing position without having to move the
cursor.

|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows the user to lookup a word in the dictionary while editing
and have it inserted in the document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FIND function key and <W> for Word
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor at the point where the word is to be inserted.
Press FIND function key followed by a <W>. You will then be prompted
for the beginning letters of the word you are looking for. Enter one or
more letters remembering that TK-WRITER will display all words in the
dictionary that begin with the letters you entered. The more letters,
the smaller the list.
Move the cursor to the word to be selected and press RETURN. The selected
word will be inserted at the cursor position. You may have to page
through the dictionary using the NEXT SCREEN, PREVIOUS SCREEN and FIRST
SCREEN function keys if necessary.
Press the EXIT function key if the word is not found or you choose not to
select it.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Returns control back to the TK-WRITER Main Menu.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
EXIT function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Use this to leave the Editor and to return to the menu.
Upon exit TK-WRITER performs the following:
|
| | 1. |
It removes any blank lines at end of document.
| | 2. |
Scans for any ~ S, ~ N, ~ A and ~ $ print control
characters in the first 50 lines of document. If found, it will continue
scanning in increments of 150 lines at a time.
| | 3. |
Performs encryption of document if encryption is specified.
|
If your document is fairly long, you may experience a short pause during
these operations.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows the user to find the beginning, end, page or line in the
document. Also reports the current location of the cursor
and provides access to the extended character set and dictionary.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FIND function key, and
Line Number, or
<P> and Page Number, or
<B> for Beginning, or
<E> for End, or
<S> for Symbol Table, or
<W> for words in dictionary.
|
| How Is It Used: |
There are four main purposes of this function:
|
| | 1. |
To report the current cursor position with respect to the left
margin, beginning of the document (line #), and page number.
| | 2) |
To allow quick movement to the beginning of the document (B), end
of document (E), a particular line number (xx) or a certain page number
(Pxx). Note that the page number is determined by referencing the page
numbering of the last printout or pagination preview.
| | 3) |
To allow access to an extended character set that may not be
available on the keyboard. This is primarily used for the multi-national
character set, but the other symbols may also be used if available on your
terminals and printers.
| | 4) |
To lookup a range of words in the dictionary.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Permits printer parameter changes such as fonts, print position, or
character spacing to be made at various places in the document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
SELECT function key followed by "F"
|
| How Is It Used: |
The steps necessary to select a font or other printer parameter changes
found in the font tables are as follows:
|
| | 1) |
Move cursor to position where the printing change is to be made.
Remember that the font change marker takes one space and will erase the
current character that is under the cursor.
| | 2) |
Press the SELECT function key followed by a "F". The font table
will pop-up.
| | 3) |
Use the NEXT PAGE and PREVIOUS PAGE function keys to page through
the entries in the font table. Point to the desired selection using the
CURSOR UP or CURSOR DOWN keys. Select it by pressing RETURN or exit the
font selection by pressing EXIT.
| | 4) |
A font change marker will be inserted into the document at the
cursor position. You may review your selection by pointing to the marker
in the document with the cursor key and then by using the SELECT key
followed by "F" to recall you selection. The marker may be removed by
either spacing over it or with the DELETE CHARACTER key.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Provides quick movement of the line either left, right, centered,
up or down.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FORMAT LINE function key, and
<L> for Left Justified
<R> for Right Justified
<C> for Centered
<A> for Advance one line - no changes
<U> for Up one line
<D> for Down one line
<T> for Tables
|
| How Is It Used: |
The left and right format commands are with respect to the current
typing template.
The center command moves the text according to the hard margins (template
1).
Moving text up and down is a quick way of interchanging lines, either with
the one above or below.
The advance function is to enable one or more lines to be skipped during
the format procedure without having to exit the FORMAT LINE function.
The Tables function allows a column to be edited as a column. See the
description under TABLE OPERATIONS.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Returns the Editor to the beginning of the current document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FIRST SCREEN function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Selecting this command will cause the Editor to move to the first
screen of the document.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Provides a quick reference of TK-WRITER.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
HELP function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
The help screens provide context sensitive documentation concerning
the various aspects of TK-WRITER. This means that the help screen will be
different depending upon where you call it up. From the initial screen,
you may then call upon other screens to obtain more information.
Once the help screen is displayed, you may perform the following
operations:
Press the EXIT key to return to the previous operation.
Point to one of the highlighted options listed in the help text and press
RETURN to branch into other help screens.
Press the NEXT SCREEN and PREVIOUS SCREEN function keys to move forward or
backward through the help screens.
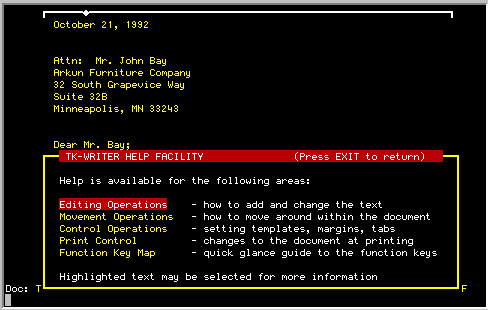
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Makes it easy to hyphenate the last word of the line.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
SELECT key followed by "W" for word wrap mode. Press successive "W"
characters until the word wrap mode is equal to "HYP" for hyphenation.
|
| How Is It Used: |
In the hyphenation mode of word wrap, TK-WRITER stops at the end of
the line if the word to be automatically wrapped to the next line is six
or more characters in length. It will beep at you for each additional
character you type indicating that the word needs to be broken before you
can continue.
Indicate where the word is to be hyphenated by moving the cursor to the
first character of the word that is to be wrapped to the next line. A
hyphen will automatically be inserted at that point.
Press RETURN at the end of the line if the word is not to be hyphenated.
The entire word will be wrapped to the next line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows new text to be inserted while typing.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
SELECT key followed by "I" for Insert Mode. The INSERT MODE toggles
ON and OFF with the "I" key.
|
| How Is It Used: |
With the INSERT MODE ON any character at the cursor position as well
as all of characters to right of the cursor will be moved to the right as
you type. If the line becomes full, one word at a time will be removed
and will fall to the next line.
The <RETURN> key behaves differently when the INSERT MODE is ON.
Each time you press the <RETURN> key the current line will be split
at the present cursor position and the remainder of the line will be
repositioned on the next line (as in CUT LINE). The cursor will jump down
to the beginning of the next line. Pressing <RETURN> on blank lines
will insert a blank line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows text saved by the MOVE TEXT or COPY TEXT commands as well as
external text from other sources to be inserted at the current cursor
position.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
COPY/MOVE/INSERT function key, and
<I> to INSERT
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor where the text is to be inserted. The line on
which the cursor resides will be pushed down to accommodate the new
text.
Press the <COPY/MOVE/INSERT> key and type <I> to insert. You
will be asked to enter the name of the text to be inserted, which is the
name that was assigned while using the MOVE TEXT or COPY TEXT commands.
If the COPY or MOVE operation was performed during the current editing
session, the most recently used name will be shown as the default and can
be selected by pressing <RETURN>.
If there is no default, or the default does not represent the text to be
inserted, enter the appropriate name and press <RETURN>. The text
will be inserted at the cursor position.
TK-WRITER will ask whether the inserted text is to be deleted under the
name used. If you have no future need for it, answer yes with a <Y>.
If you answer no, the text will be saved for use at some later time.
To see the entire list of existing text names, press the <^>
key. A pop-up menu will display the name of each copied or moved text
and you will be able to select the appropriate entry by pointing to it and
then pressing <RETURN>. Press the <EXIT> key to return without
any selection.
More than one section of text can be inserted at once by entering a list
of text names separated by a <+>. For example, if a form letter was
to be created consisting of an address, salutation and body, the following
might be used.
ADDRESS+SALUTATION+BODY
All three sections would be assembled on the screen for you. Note that
you can have any number of sections from which to choose.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Enables a line of text to be quickly justified to the left margin.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FORMAT LINE function key,
<L> for LEFT JUSTIFY
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor on the line that is to be justified and press the
<FORMAT LINE> key.
Pressing <L> will cause the line to be left justified with respect to
the current templates left margin. When completed, the cursor will move to
the next line. Press <L> again if the new line is also to be left
justified.
Press <RETURN> to return to Edit Mode.
The left justify function is a quick way to realign text on a new template
without actually reformatting the text.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Removes an entire line from the document at the current cursor
position and moves all following lines up one line.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
DELETE LINE function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor on the line that is to be removed and press
<DELETE LINE> key. The line will be removed and all subsequent
lines will be moved up to take its place. The cursor remains in the same
position.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
To add lines. boxes and polygons to the document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
SELECT function key
<L> for Line Drawing
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor on the line and column where the line drawing is
to begin. Enter the line drawing mode with the SELECT function key. Draw
the lines by using the up, down, left and right cursor keys.
Moving the cursor through already existing text or lines will replace it
with a new line. Line intersections will be automatically created.
The alphanumeric keys are not available for normal typing although they
can be used to cycle through the available line drawing characters.
The line drawing mode will be cancelled by pressing any other function
keys other than the cursor keys. After a short pause, you will resume
the edit mode.
As with underlining and bolded text, any editing performed within the
actual line drawing will cause it to be removed.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Inserts a new blank line at the current cursor position.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
INSERT LINE function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor on the line that is to be moved down and press
<INSERT LINE> key for each line to be inserted in the document.
Note that if you insert many lines, the document may have to go through a
document renumbering. This is an automatic procedure that TK-WRITER
performs to restructure it's internal numbering format. TK-WRITER will
display a "please wait" message as this may take a few moments to
accomplish.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows the user to move quickly to the next word, sentence, paragraph
or end of line.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
NEXT WORD, NEXT SENTENCE, NEXT PARAGRAPH or END-OF-LINE function keys
|
| How Is It Used: |
Press these function keys to move quickly from section to section
within the document. TK-WRITER uses the text format to determine the next
location to move to as follows:
NEXT WORD looks for a space character or beginning of line.
NEXT SENTENCE looks for either a period, exclamation mark or question
comma followed by two spaces or the beginning of the line.
NEXT PARAGRAPH looks for a blank line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
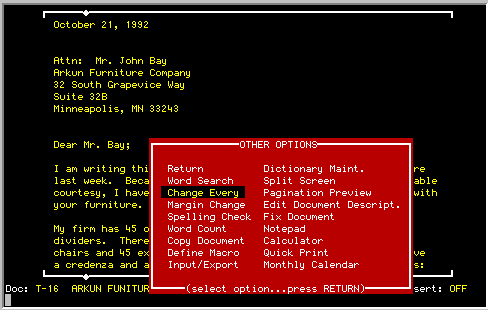
Allows the user to record a specific editing sequence and play it back
at any point during the editing process. These macros may be temporary
and only used for the one occasion, or they may saved in macro files for
use at a later time.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
OTHER OPTIONS function key, select MACROS from the OTHER OPTIONS menu
|
| How Is It Used: |
To Record a New Macro:
|
| | 1) |
Move the cursor to the point in the document where the recording
is to begin and then select the MACRO option in the OTHER OPTIONS menu.
| | 2) |
Select DEFINE MACRO option in the MACRO OPTION screen. It will prompt
you for the macro name. Enter one of the following:
no name - a temporary macro played back by pressing the HOT
function key (Control A).
0-9 - a temporary macro that can be played by entering the
number and then the MACRO KEY.
Alpha name - An alphabetic name that begins and ends with a
letter of the alphabet. These are permanent macros and are stored the
default macro file listed on the bottom right of the status line.
AAAAA.MMM - An alphabetic name as above, but followed with a
period and the Macro File to in which to store the macro.
| | 3) |
After the name is entered, a message will appear indicating that
the recording will begin after pressing the RETURN key. Press RETURN. A
macro record mode message will appear on the bottom line and every
keystroke, whether a function key or normal typing sequence will be saved
in the macro buffer. Press the MACRO function key to terminate the macro.
The macro is now available for use anytime during the editing process.
|
Note: All keystrokes may be recorded except HELP screen calls,
the DEFINE MACRO command, and external calls to other packages. You
may bring up help screens during the record mode for a quick reference
without it being recorded in the macro.
To playback the macro:
|
| | 1) |
Move the cursor to the point in the document where the macro is to
take effect.
| | 2) |
Enter the macro name (and optional Macro File name if needed).
Press the MACRO key. If the name is found it will play back the macro and
leave the cursor at the end of the macro.
|
If no macro file is specified, TK-WRITER will search the default macro
file listed on the status line first. If it isn't found there, it will
search the "sys" macro file. If it still isn't found, the a beep will be
sounded and nothing will be changed.
If a macro file is specified, TK-WRITER will first search the specified
macro file, then the "sys" file.
The temporary macros are lost when the edit mode is completed and you
return to the TK-WRITER menus.
There are two different ways of editing macros that were previously
recorded:
|
| | 1) |
Select the Macros option in the OTHER OPTIONS menu. Then select
Edit Macro, the appropriate Macro File, and the desired macro. The macro
will be displayed on the screen for you to edit.
| | 2) |
The entire Macro File can be edited by selecting the "~G" directory in
the Directory Options. Each macro is listed in the file with the name of
the macro listed on a line by itself (preceded with a period character
".") followed by one or more lines of the macro. Using this method will
enable you add new macros to the file.
|
See Section 2 for more information concerning editing macros.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Permits the length of the line (maximum width of the document) to be
changed while editing.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
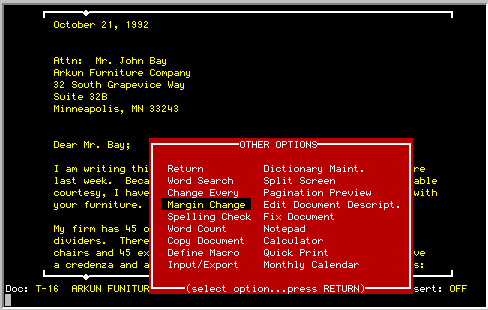
OTHER OPTIONS function key, select MARGIN CHANGE from Other Options
menu
|
| How Is It Used: |
Press the <OTHER OPTIONS> key and select the
MARGIN CHANGE option. TK-WRITER will request the new line length. Enter
a number from 5 to 126 and press <RETURN>.
You will then be asked if you want the text to be adjusted to the new
margins. If you reply by pressing <Y> for YES, the document will be
adjusted to the new line length on a paragraph by paragraph basis.
Remember that the word processor assumes that all paragraphs are separated
by a blank line. If there are no blank lines between paragraphs and you
approve the adjustment of text to the margins, all of text will be run
together as if it was one paragraph.
|
MOVE TEXT |
|
| Purpose: |
Enables one or more lines of text to be moved to another position in
the same document or any other document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
COPY/MOVE/INSERT function key, and
<M> for MOVE
|
| How Is It Used: |
Move the cursor to the first character to be included in the move
operation. Press the <COPY/MOVE/INSERT> key and select the MOVE
TEXT command by pressing <M>. You will be asked to highlight the
text to be moved by using the cursor keys. The action taken by each
cursor key is as follows:
|
| | Left |
Removes one word from the text to be moved, and changes it back to
low intensity.
| | Right |
Adds one word to the text to be moved and highlights it.
| | Up |
Removes a whole line from the text to be moved and changes it
back to low intensity.
| | Down |
Adds one line to the text to be moved and highlights it.
|
Notice that left and right cursor keys provide word control,
while the up and down cursor keys provide line control. After a
little practice, you will be able to quickly highlight a region of text
using the appropriate cursor keys.
Press <RETURN> after you have highlighted the text to be moved. The
text will be removed from the document.
It is then necessary to assign a name to this highlighted text. Use a
name that will be easily remembered if you are likely to use this moved
text over and over again. You may use the 26 letters of the alphabet and
the 10 numbers. Press <RETURN> when the name is entered.
You will then be reminded that you can insert the highlighted text with
the INSERT TEXT command using the name that you assigned. Press RETURN
to return to the edit mode. See INSERT TEXT for information concerning
inserting the text in the current document or in another document.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Enables the cursor to be quickly moved to the first blank space at
the end of a line.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
MOVE TO END-OF-LINE function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
By pressing this function key, the cursor will jump to the first
space following the last word or character on the line. This positions
the cursor for the entry of additional text on the line.
If no space remains at the end of the line, the cursor will automatically
move to the next line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Advances the display of the document forward one screen.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
NEXT SCREEN key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Each time the <NEXT SCREEN> key is pressed, the next 21 lines
of the document are displayed and the cursor is repositioned to the top of
the screen.
When the end of the document is reached, blank lines will be displayed and
added to the end of the document. Any remaining blank lines at the end of
the document will be removed when the EXIT command is issued.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Advances the display of the document back one screen.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
PREVIOUS SCREEN key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Each time the <PREVIOUS SCREEN> key is pressed it will cause
the 21 lines of text preceding the current screen to be displayed.
If the beginning of the document is reached, the command is inoperative.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Provides a temporary left margin for indented text.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
SELECT function key + <Q>
|
| How Is It Used: |
In order to create a temporary left margin:
|
| | 1) |
Position the cursor where the indent is to begin.
| | 2) |
Press the SELECT key followed by <Q>.
| | 3) |
Type indented material. The text will wrap within the new left
margin and the current template will still govern the right margin.
| | 4) |
Finish the indent by pressing RETURN twice. The cursor should go
back to the left margin of the current template.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows a paragraph to be adjusted to fit the current margins or user
selected margins.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
REFORMAT PARAGRAPH function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Remember that the word processor assumes the paragraphs are separated
by a blank line. This command performs an adjustment from the cursor
position to the end of the paragraph.
There are two options provided with this command. You may either select
the current typing template for the outside boundaries for the new text,
or you can enter new values. Select the current template by typing a
<Y> for YES. Type a <N> for new margins. Pressing
<RETURN> without a response will return Edit Mode without further
action.
If you choose the current margins, the new text will be reformated so that
it will fill the margins of the current template.
If you choose to specify the margins, you will then be asked for the
number of spaces on the left and right. Enter the number of spaces the
text is to be indented from the left and right margins of the screen.
(You may substitute the right margin with the width of the text by
entering "+" followed by the desired width.)
The reformating will take place on the screen. When completed you will be
returned to Edit Mode. If the paragraph continues on to the next screen
the remainder of the reformating will not be seen, and a Wait
Message will be displayed temporarily.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Provides a quick means to move the cursor to the first position of
the next line. Also is used to terminate input to a number of commands.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
RETURN key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Pressing the <RETURN> key while editing will cause
the cursor key to be positioned at the left margin of the next line. If
the next line is on the next screen, a single line scroll will take place
moving the screen up one line.
If the INSERT MODE is ON while editing a document, a <RETURN> key
will cause the line to broken at the cursor position. Remaining text on
the line will be carried forward to the next line. In other words, the
<RETURN> key functions the same as the CUT LINE function.
The <RETURN> key is also used to terminate the input of parameters to
the various commands. In most circumstances it will return the user to
Edit Mode if no entry is made.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Moves the text on the line to the right until it is flush with the
right margin.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FORMAT LINE function key, and
<R> for Right Justification
|
| How Is It Used: |
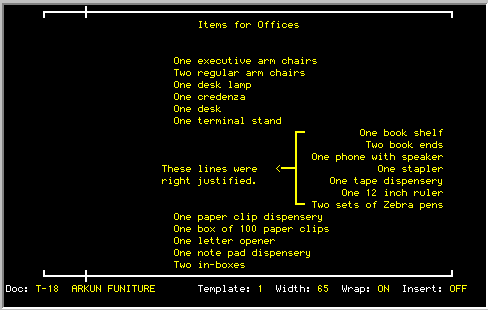
The RIGHT JUSTIFICATION command allows the user to position the line
to the far right of the current template. Dates, addresses, headings and
other text that needs to be on the right margin can be easily moved over
using this function.
After the <R> key is pressed for RIGHT JUSTIFICATION, the text on the
current line will be adjusted to the right margin, and the cursor will
move move down one line. When the last line of the screen is reached,
the screen will scroll up one line. Pressing another <R> will cause
the next line to be right justified and so on. Press <RETURN> to
return to the edit mode.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Provides a quick scan for misspelled or unknown words in the document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
OTHER OPTIONS function key, and select SPELLING CHECK from Other
Options menu
|
| How Is It Used: |
The Spelling Check option compares each word in the document against
the dictionary built into the TK-WRITER. Any words that are not found or
are misspelled are reported to the user. The user has the following
options when such a misspelled word is encountered:
|
| | Skip |
Pressing an <S> indicates that the current spelling is going
to be kept and the spelling check should skip to the next word.
| | Correct |
Pressing a <C> indicates the current word should be corrected.
The user will be instructed to enter the correct spelling of the word and
then the word will be corrected on the screen. Note that only this
occurrence of the word will be corrected.
| | Learn |
Pressing a <L> will cause the word to be inserted in the
dictionary for future use. In this way the dictionary will learn your
particular vocabulary.
| | Ignore |
Pressing an <I> will cause the current word to be ignored for
the remainder of the Spelling Check scan. May be used to skip proper
nouns that are used repeatedly during the document.
| | Dictionary |
Pressing a <D> will allow you to lookup a word in the spelling
check dictionary (word list). It will ask you to enter the first letters
of the word that you are looking for.
| | Return |
Pressing an <R> will cause the Spelling Check option to be
aborted and the control will be returned to the edit mode.
|
All words will be stripped of punctuation and upper case letters will be
converted to lower case before being compared to the dictionary.
Therefore, although proper nouns may be inserted in the dictionary, the
use of capitalization will not be checked.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows the user to select characters that are available in the
extended character set.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
Control W, Control Z or Control B
or
FIND function key and <S> for Symbols
|
| How Is It Used: |
The extended character set is a group of symbols that fall in the
ASCII character set range of 128 through 255. These special symbols may
be used to select characters used in the major European languages as well
as other graphic characters not part of the standard 7-bit ASCII codes.
In order to use these extended characters the MUMPS operating system,
communications, terminal and printer must all support 8-bit character
encoding. Generally this is an option that may be selected in setup. In
addition, the terminal and printer must support either the DEC
multinational, PC-850 or Roman-8 symbol sets. TK-WRITER will provide the
necessary translation from one symbol set to the other if needed.
|
| | NOTE: |
TK-WRITER uses the PC-850 code page for the IBM PC compatible
devices. Your PC may be setup to use a different code page (typically 437
in the US). This generally will not be a big problem as there are many
similiarities between the various code pages, but you may see strange
symbols when TK-WRITER automatically converts symbols from one type to
another. Although code page 850 is not necessarily the best, it does
contain a broad range of the multi-national characters. See your DOS
manual on how to change the code page.
|
There are four ways of accessing the special symbol sets that are
available on many terminals and PCs:
|
| | Direct |
Special national keyboards will allow direct access to these
symbols by pressing the appropriately marked key. This is the preferred
way if you use these symbols quite often.
| | Compose |
You can build the special symbol by either using the COMPOSE
function key of TK-WRITER or a hardware compose sequence that is built
into some terminals. See COMPOSE Key.
| | Replacement |
An individual vowel may be replaced with its alternate forms by moving
the cursor to the vowel and pressing either Control W, Control Z or
Control B (depending upon your operating system and terminal type).
TK-WRITER will cycle through all the alternate forms. Stop on the
desired character.
| | Table Lookup |
You may view the entire table and make a selection by pressing the
SELECT function key and <S>. Once the table is displayed move the
cursor to the desired symbol and press RETURN. Press the EXIT function
key to return without a selection.
|
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows you to easily edit text when it is in columns.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
FORMAT LINE function key and
"T" for Tables
|
| How Is It Used: |
This function will work on columns of text starting on the line that
you are on when you enter and proceding to either a blank line, hard page
break, a change to the format of the table, or the 99th line, whichever
comes first.
After the table is sized and marked you will be shown a list of TABLE
OPTIONS as illustrated in the screen below:
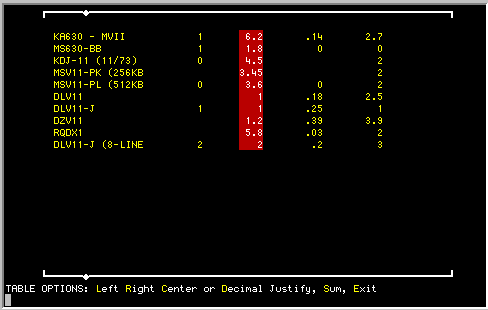
Use the <NEXT SCREEN> and <PREVIOUS SCREEN> functions keys to
move the highlighted column marker from column to column. This marker
indicates on which column the table commands will operate (it only works
on one column at a time). Notice that the marked columns are marked with
a column width that encompasses the left-most-edge and the right-most-edge
of the column. This is the column width and these boundaries are used in
the following options:
|
| | Left |
Left justifies column within the boundaries of the column.
| | Right |
Right justifies column within the boundaries of the column.
| | Center |
Centers column within the column boundaries.
| | Decimal |
Aligns column on the decimal point. The decimal point is
assumed on numbers without a decimal point. You will be asked to enter
the number of allowable places to the right of the decimal point.
Leaving this blank will leave the numbers as is; a number from 0-9 will
automatically redisplay the numbers with the desired digits to the right
of the decimal point. Rounding is performed on the number as is
necessary. Note that this command changes the values of the numbers
according to your instruction. There is no provision for restoring
original values if digits are removed.
|
The CURSOR KEYS are also active in the TABLES MODE and work as follows:
|
| Cursor
Right |
Moves the column one place to the right. If the column bumps against
another column to the right, they will exchange positions.
| Cursor
Left |
Moves the column one place to the left. If the column bumps against
another column to the left, they will exchange positions.
| Cursor
Up |
Rolls the contents of the column up one line. The top line will be
wrapped around to the end of the column.
| Cursor
Down |
Rolls the contents of the column down one line. The bottom line will
be wrapped to the top of the column.
|
A SUM function will add all the items within the column and report the
total on the bottom status line. (You can insert it into your document by
pressing the REPEAT KEY.) All non-numeric characters are ignored.
Use either the "E" option or the <EXIT> function key to return to
the edit mode.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Moves the cursor quickly to preset columns on the screen.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
TAB key
|
| How Is It Used: |
The <TAB> key is used in conjunction with the <TAB SET>
and <TAB CLEAR> functions to enable the rapid movement of the cursor
to preset locations. Tabs may be set for each template. Switching from
one template to another will allow the user to have a number of different
tab settings.
The default template #1 has a tab set at the fifth column. The user must
set any other tab stops as are necessary. The tab stops are indicated by
a vertical line displayed on the top and bottom margins.
Each time the "TAB" key is pressed the cursor will jump to the next tab
stop on the line. When the last tab stop is encountered, the cursor is
then returned to the left margin of the next line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Removes a tab stop from the template.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
TAB SET/CLEAR function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Move the cursor to the tab stop that is to be removed and press the
<TAB SET/CLEAR> function key. The vertical lines at the top and
bottom margins will be removed and the tab stop will no longer be
functional.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Sets a tab stop at the column where the cursor is currently
positioned.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
TAB SET/CLEAR function key
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor where a tab stop is desired and press the <TAB
SET/CLEAR> function key. Vertical lines on the top and bottom margins
indicate where the tabs are set.
|
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows for various input formats and tab settings.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
SELECT function key, and
<T><C> for Template (Create) , or
<1> through <9> to select a template, or
<R> to review current templates
<RETURN> to select template defined for current cursor position
|
| How Is It Used: |
Typing Templates provides the user with a convenient way to change
the typing margins or tab stops. Up to nine different templates may be
defined. The default template is number one and always contains the left
and right margins defined by the line length.
You may display all of the currently defined templates for your document
by using the <R> parameter. It will list out each template on the
screen as in this example:
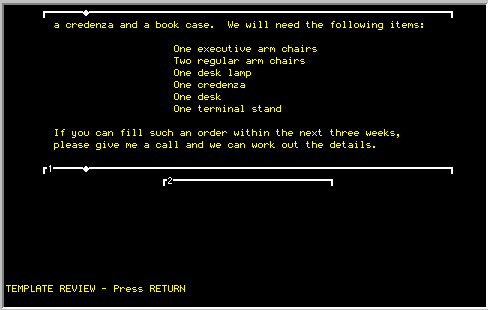
The user may create other templates (2 - 9) by using the <C>
parameter. The left and right margins are requested and are always the
number of spaces inside the the left and right margins indicated on the
sides of the screen. In other words, the user may only create formats
that are equal or shorter in line length than the original template.
An alternate method of entering the right margin is to enter a "+"
followed by a number representing the number of spaces to the right of the
new left margin. This allows you to define the left margin at a
particular indentation, and then enter a value indicating the total width
of the new template.
The general use for templates with different margins is for indented text
such as quotations or lists. The advantages of setting up a new template
for indented text is that the Word Wrap and Reformat Text options use the
margins of the current template. The user can therefore type in a new
format with all of the conveniences of the original template without
having to indent or tab at each line.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Enables text to be underlined both on the screen and when printed.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
BOLD/UNDERLINE function key, and
<U> for UNDERLINE followed by
<C> for CHARACTER, or
<W> for WORD, or
<P> for PHRASE
|
| How Is It Used: |
Position the cursor on the first character of the word or phrase to
be underlined and press the <BOLD/UNDERLINE> function key. Press
<U> for underline and one or more of the following to underline
the appropriate text:
|
| | C |
underlines a single character
| | W |
underlines a single word and advances the cursor to the first letter
of the next word. The space between the words is not underlined.
| | P |
underlines the current word and one space following the word. The
cursor is positioned on the next word. Use the <P> key to underline
a phrase where the spaces between the words are also to be underlined. End
the last word of the phrase by pressing the <W> key so that the space
at the end of the phrase will not be underlined.
|
Press <RETURN> to end the underline mode and to return to the edit
mode
Underlining may be removed from the text by retyping one or more
characters within the underlined area and then moving the cursor.
See also SELECT UNDERLINE/BOLD for underlining new text as it is typed.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Counts the number of letters, words, lines and paragraphs for a part
or all of the document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
OTHER OPTIONS function key, and select WORD COUNT from Other Options
menu
|
| How Is It Used: |
Select count for paragraph by pressing <P> or count for the
entire document by pressing <D>.
The results of the count are shown on the bottom of the screen. The
number of paragraphs shown indicate the number of areas of text that are
separated with a blank line, whether they are a paragraph or not. The
letter, word and line count are the actual results of the count.
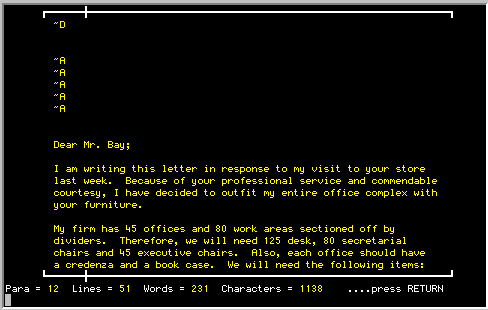
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Provides a means for quickly searching for a word or phrase in the
document.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
OTHER OPTIONS function key, and Select WORD SEARCH, and press RETURN
|
| How Is It Used: |
Select the WORD SEARCH option under OTHER OPTIONS menu. You will be
asked to enter the word or phrase to look for in one of the following four
formats:
|
| | xxxx |
provides exact match of word xxxx
| | xxxx.. |
looks for all words beginning with xxxx
| | ..xxxx |
looks for all words ending with xxxx
| | ..xxxx.. |
looks for any occurrence of xxxx regardless of position in word
|
then press <RETURN>. You will then be asked whether the search
should start at the current line number or at the beginning of the
document. Enter <B> or <H> accordingly.
The search starts at either the beginning or at the current line and
proceeds through the document until a match is made or the end of the
document is found. If a match is found, the cursor will be at the
beginning of the word whose match was found. To continue the search,
press the <REPEAT> function key.
Pressing the <RETURN> key anytime during the search process will end
the search and return the user to Edit Mode.
|
|
|
| Purpose: |
Allows the user to select the type of word wrap that is to be used
during the edit mode.
|
| Type Of Operation: |
Editing
|
| Keystroke(s) Required: |
TYPING CONTROL function key, and
<W> for Word Wrap mode
|
| How Is It Used: |
Pressing a <W> in TYPING CONTROL function will toggle the Word
Wrap Mode from ON to OFF to HYP and then back to ON.
The three Word Wrap Modes are used as follows:
|
| | ON |
The Word Wrap option will automatically wrap the cursor to the
next line when the end of the line is encountered. It will bring the
current word around with it and insert it at the beginning of the line.
| | OFF |
The cursor still wraps to the next line, but the current word
is not brought along with it. The word will be broken at the end of the
line and any other letters will be found on the next line.
| | HYP |
This mode will behave just as in ON above except when there is
more than 5 characters in the last word of the line. It will stop and
beep on each successive keystroke until you move the cursor back with the
<CURSOR LEFT> key to indicate where to hyphenate the word. Point to
the first character to be wrapped to the next line. TK-WRITER will
automatically add a hyphen character.
|
The Word Wrap Mode may be changed at anytime. The document will always be
initialized in the Word Wrap Mode specified in the document parameters.
|